Debt and real estate, a game worth 137 billion
20 January, L’Economia
93 billion euro. This is the value of the real estate assets that, at the end of the first semester of 2017, were put as guarantee of non-performing loans. This estimate comes from the report by PwC “The Italian NPL Market”, from which the charts are taken. According to the survey, the secured loans represent 49% of the total gross bad loans, equal to 200 billion euro.
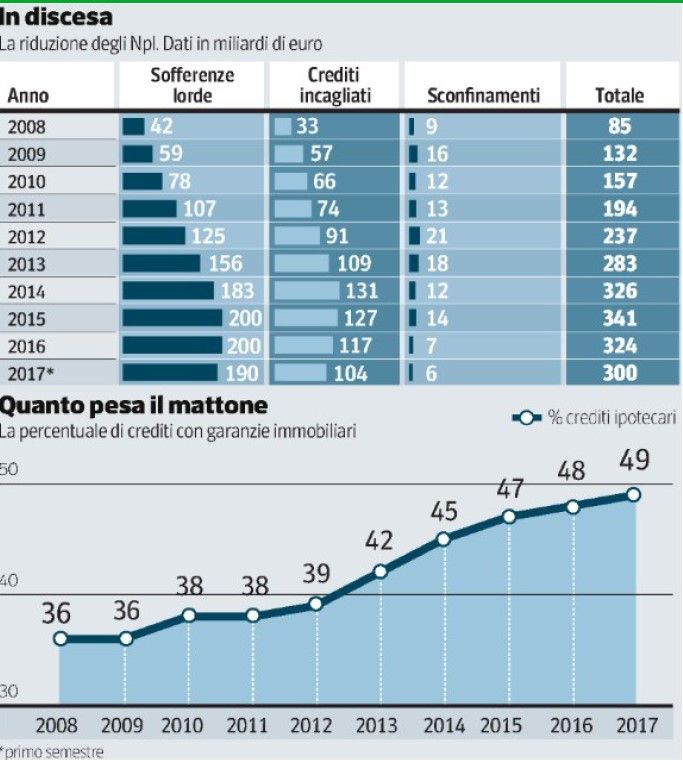
To this amount, already very high, we must add the value of real estate assets put as guarantee of impaired loans and about to become bad loans and overdrafts. The total exposures amount to about 110 billion euro. Assuming a cautious estimate for a 40% quota of secured impaired loans, the total of real estate guarantees would amount to approximately 137 billion.
The alternatives
Servicers cover a fundamental role in the disposal of impaired credits since they receive the bad loans from banks through securitisations. DoBank, a subsidiary of Italfondiario, is the leader in the sector: the company manages bad loans for 77.5 billion, 61 of which is backed by real estate. The securitisation obviously happens at a much lower price compared to the nominal value of the credit. According to the last estimates by Ifis, real estate guarantees at the end of the second quarter of 2017 were generally exchanged for the 33% of the original book value. The quota has in the last year due to the offer surplus and the still uncertain perspectives of the market. However, to make a comparison, we must keep in mind that the unsecured credits are exchanged for 13% of their nominal value.
Regarding real estate assets, the servicer makes an accurate analysis of the conditions of each asset and, whenever needed, carries out also the maintenance works to put the property on the market at the best conditions possible. For this reason, the role of rating agencies is essential since they make an assessment of the price that can be realistically obtained at the current market conditions. The following phase consists of selling the assets employing various strategies. In the case of a corporate buildings, for instance, the so-called Patto Marciano can be used, namely putting the asset for sale at a price estimated by an evaluating third party, if the sale is successful and the amount obtained is higher then the debt, the debtor will get the difference; in case the amount is lower, the debtor will have his exposure cancelled anyway.
In case none of these two strategies is applicable, the only other way left is to go through a judicial auction. Today, judicial auctions are quicker and the procedures smoother, making possible for debtors to obtain excellent earnings. However, if the price is lower than the debt and the related costs, the debtor will be still insolvent for the difference.
Source: L’Economia
Translator: Cristina Ambrosi

 Portugal
Portugal  Spain
Spain  Greece
Greece 



